|
Mainland High School
Suitable for a Disaster: ISTF 08-1835 |
||
|
Home
Introduction Contest Components One Two  Product Product
Three Fabrics History of Fabrics Smart Fabric Projects Sensors Nano Sensors Power Production Communication Cell Phones 3G Phones Data Transfer Helikites Interoperability Microwaves Relief Agencies Telecommunication Project Assessment Team |
Interoperability
Our governmental examples of interoperability include SAFECOM, GAO,and e-GIF. All
of these are attempts to standardize protocol or force the use of a universal proccess.
 SAFECOM is a program of
the Department of Homeland Security dedicated to communications interoperability
for emergency responders. They are backed by the
Office of Emergency Communications and the Office for Interoperability and
Compatibility. SAFECOM is a program of
the Department of Homeland Security dedicated to communications interoperability
for emergency responders. They are backed by the
Office of Emergency Communications and the Office for Interoperability and
Compatibility.
They have defined interoperability as the ability of every standard, procedure, or format to communicate between each other. Interoperability can be hindered by:
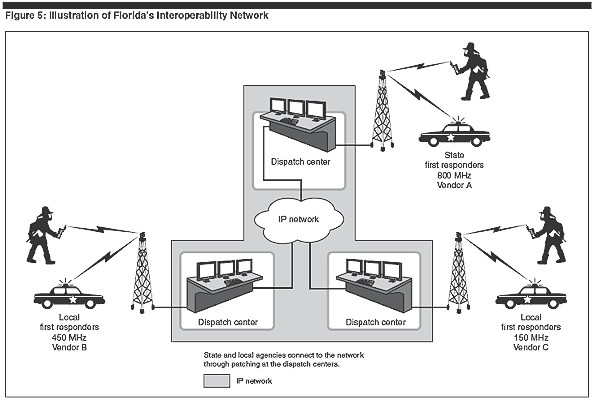
The Government Accounting Office, GAO, conducted interoperability research on grants that the Department of Homeland Security awarded. This research was conducted in Congress' request to see how the grant monies were being used and to determine the development and implementation of interoperability. As a result of their research they recommended that the Department of Homeland Security give states assessments on their use of the grants and give guidance on acquiring interoperable equipment. The Department of Homeland Security gave Florida a 55.7 million dollar grant to develop a system of interoperability. In response, Floridaian government established a committee to decide how the money should be spent. It was determined that completely replacing the old system with a new system would cost too much. Instead, they established a dispatch center that receives and translates signals and redistributes them to relevant personnel. Florida's government also established a mobile version called Mutual Aid Radio Communications who are equipped with their own radios to be deployed to first responders. Radios are deployed when local communications are down, or, when neighboring states have need during emergenices such as hurricane Katrina. e-GIF, a current project in the United Kingdom, defines interoperability as the ability of government organizations to share/integrate information and business processes by using common standards. e-GIF, which is short for electronic Government Interoperability Framework, is a set of policies and standards which will allow information to be shared seamlessly with the public. The framework will provide citizens and businesses with better access to modern and improved public services. The e-GIF will reduce costs and risks, and allow organizations to concentrate on providing information and services to their customers. The standards that the e-GIF endorses remain accessible to everyone free of charge. Aspirations of the e-GIF include:
 OnStar is a device that allows drivers or passengers in danger to call for help
and be located if he or she does not have the time or ability use a cell phone.
The system incorporates many different
technologies such as GPS, cellular phone, and emergency response systems.
The OnStar console contains a built-in microphone and utilizes the car's speakers.
When a car's occupant makes a call, one merely says the number or a name associated
with the number and the OnStar console calls on its own allowing the occupant the
speak "hands free." The Vehicle Comm and Interface Module (VCIM) within the car
connects the vehicle to OnStar's Call Center. Not only does OnStar make it easier
to make calls, but it guarantees better cellular reception. It uses a full 3 watts as opposed to a cell phone's 0.6 watts.
OnStar also incorporates voice recognition in more ways than just the telephone:
one can request information on the weather, acquire turn-by-turn directions, and
request roadside assistance. Also in the event of an accident, the OnStar Call Center
used four different satellites to pinpoint the car's location when either the driver
or the car itself asks to be located. The VCIM will translate requests into XML
(Extensible Markup Language), translate it into VoiceXML, and dictate the requested
information.
OnStar is a device that allows drivers or passengers in danger to call for help
and be located if he or she does not have the time or ability use a cell phone.
The system incorporates many different
technologies such as GPS, cellular phone, and emergency response systems.
The OnStar console contains a built-in microphone and utilizes the car's speakers.
When a car's occupant makes a call, one merely says the number or a name associated
with the number and the OnStar console calls on its own allowing the occupant the
speak "hands free." The Vehicle Comm and Interface Module (VCIM) within the car
connects the vehicle to OnStar's Call Center. Not only does OnStar make it easier
to make calls, but it guarantees better cellular reception. It uses a full 3 watts as opposed to a cell phone's 0.6 watts.
OnStar also incorporates voice recognition in more ways than just the telephone:
one can request information on the weather, acquire turn-by-turn directions, and
request roadside assistance. Also in the event of an accident, the OnStar Call Center
used four different satellites to pinpoint the car's location when either the driver
or the car itself asks to be located. The VCIM will translate requests into XML
(Extensible Markup Language), translate it into VoiceXML, and dictate the requested
information.
The OnStar buttons can usually be found on the rearview mirror, the dashboard, or the overhead console. There are a total of four buttons. The first is the power button. The second is the phone call button that you press to make cellular calls. The third is the blue OnStar button that alows you to contact a live or computer advisor in order to set up an OnStar plan. The final button is the red emergency button. Homeland Security - Welcome to SAFECOM http://www.safecomprogram.gov/SAFECOM/ Homeland Security - Office of Emergency Communications http://www.dhs.gov/xabout/structure/gc_1189774174005.shtm Homeland Security - Interoperability http://www.safecomprogram.gov/SAFECOM/interoperability/default.htm Homeland Security - Technology Solutions & Standards http://www.safecomprogram.gov/SAFECOM/library/technology/1258_statementof.htm Homeland Security - Interoperability Overview http://www.safecomprogram.gov/NR/rdonlyres/54F0C2DE-FA70-48DD-A56E-3A72A8F35066/0/Interoperability_Continuum_Brochure_2.pdf Homeland Security - Statewide Communications Planning Methodology http://www.safecomprogram.gov/SAFECOM/tools/scip/ Homeland Security - Interoperability Case Studies http://www.safecomprogram.gov/SAFECOM/library/interoperabilitycasestudies/1223_statewidecommunications.htm GAO - First Responders: Much Work Remains to Improve Communications Interoperability http://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-07-301 GAO - Florida's Interoperability Network (pg 56) http://www.gao.gov/new.items/d07301.pdf Department of Management Services - Mutual Aid Build-Out http://dms.myflorida.com/suncom/public_safety/radio_communications/florida_interoperability_network_fin/mutual_aid_build_out CabinetOffice - Frequently Asked Questions: e-GIF http://www.govtalk.gov.uk/faq/faq.asp?section=e-GIF&topic=6 networking government in New Zealand - What is the e-GIF? http://www.e.govt.nz/standards/e-gif/e-gif-v-3-3/policy/chapter2.html OnStar http://www.onstar.com/us_english/jsp/index.jsp?useFlash=N OnStar - OnStar Technology http://www.onstar.com/us_english/jsp/explore/onstar_basics/technology.jsp On Star - OnStar System http://www.productivitydevelopment.com/38%20OnStar.pdf How Stuff Works - How OnStar Works http://auto.howstuffworks.com/onstar1.htm OnStar - How Do I Use OnStar? http://www.onstar.com/us_english/jsp/explore/use_onstar.jsp OnStar - Plans & Pricing http://www.onstar.com/us_english/jsp/plans/index.jsp |